how to find functional groups in a molecule Organic chemistry classes with structure
Functional groups are essential features of organic molecules that determine their properties, reactions, and functions. These groups are specific arrangements of atoms that impart unique chemical and physical characteristics to the molecule. Understanding functional groups is, therefore, critical for predicting and explaining reactions in organic chemistry. One of the most important functional groups is the hydroxyl group (-OH), which is found in alcohols, phenols, and carboxylic acids. This group is polar and can form hydrogen bonds, making it highly soluble in water and other polar solvents. Alcohols and phenols also have characteristic properties such as high boiling points, flammability, and reactivity with strong acids. Carboxylic acids have acidic properties that can lead to the formation of salts, esters, and amides. Another critical functional group is the carbonyl group (C=O), which is present in aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters. This group is polar and electrophilic, making it highly reactive towards nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, and amines. Aldehydes and ketones have characteristic properties such as low boiling points, sweet odor, and reactivity with oxidizing agents. Carboxylic acids and esters have acidic properties and can undergo hydrolysis to form alcohols. Amino groups (-NH2) are another common functional group found in amino acids, proteins, and nitrogen-containing compounds. This group is basic and can act as a proton acceptor in acid-base reactions. Amino acids form peptide bonds through reactions between the amino and carboxylic acid groups, creating complex structures such as proteins and enzymes. Nitrogen-containing compounds such as amines, amides, and nitrites also have unique properties and functions based on the amino group. Other functional groups include halogens (-F, -Cl, -Br, -I), which confer unique properties such as reactivity towards metals, solubility in organic solvents, and reactivity with nucleophiles. Sulfhydryl groups (-SH) are present in cysteine and play a critical role in the structure and function of proteins. Phosphate groups (-PO4) are important in DNA and energy metabolism, while methyl groups (-CH3) are found in fats, oils, and hormones. In conclusion, functional groups are critical components of organic compounds that determine their properties, reactivity, and functions. Understanding the different types of functional groups and their characteristics is essential for predicting and explaining reactions in organic chemistry. By identifying the functional groups in a molecule, chemists can determine its physical, chemical, and biological properties and develop new compounds with desirable traits.
If you are searching about Organic Chemistry Classes with structure - Phartoonz you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Organic Chemistry Classes with structure - Phartoonz like 2.3 Functional Groups – Organic Chemistry I, Organic Chemistry Classes with structure - Phartoonz and also 2.3 Functional Groups – Organic Chemistry I. Read more:
Organic Chemistry Classes With Structure - Phartoonz
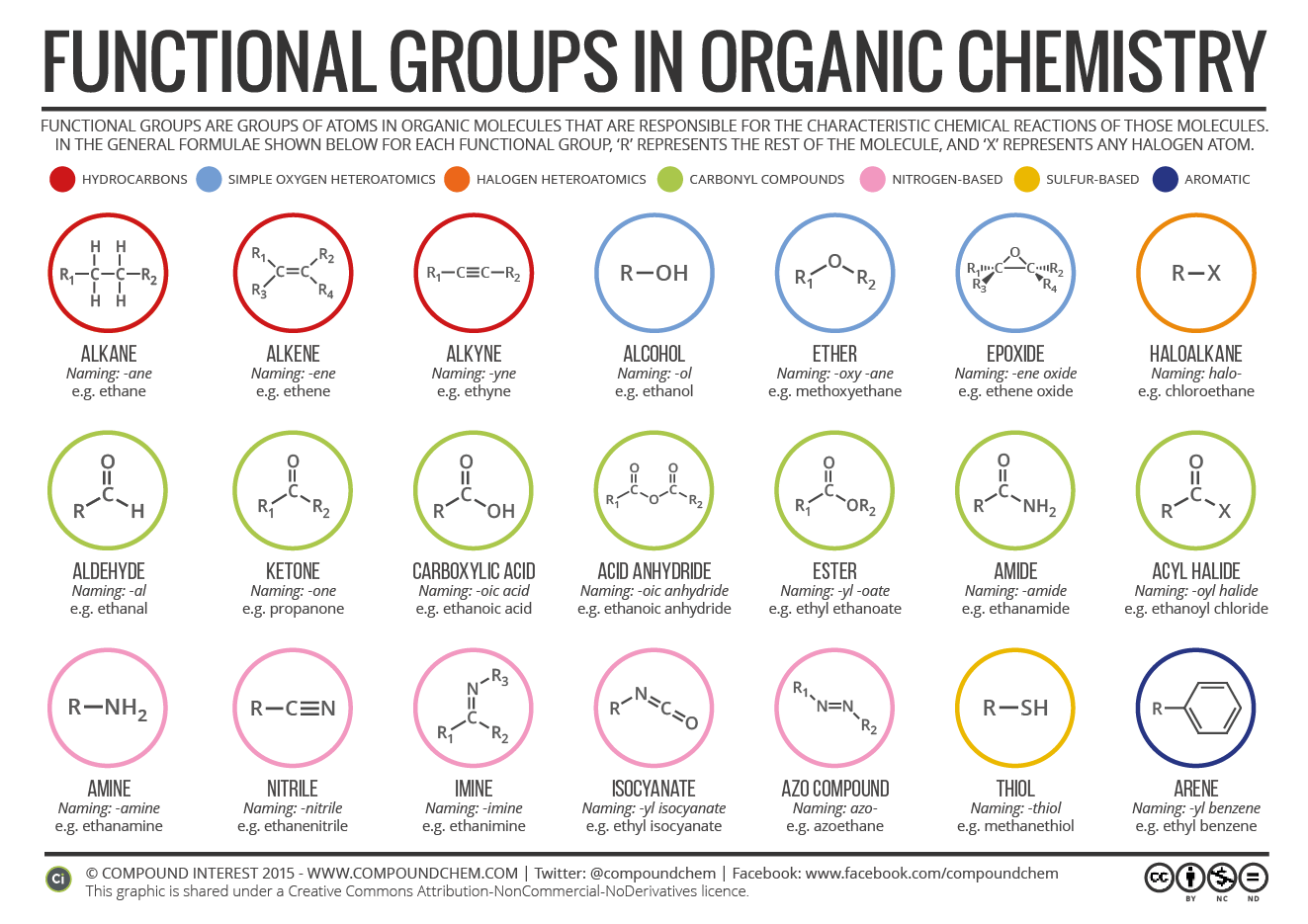 www.phartoonz.comcompoundchem
www.phartoonz.comcompoundchem
Organic Chemistry-Functional Groups - YouTube
 www.youtube.comchemistry
www.youtube.comchemistry
2.3 Functional Groups – Organic Chemistry I
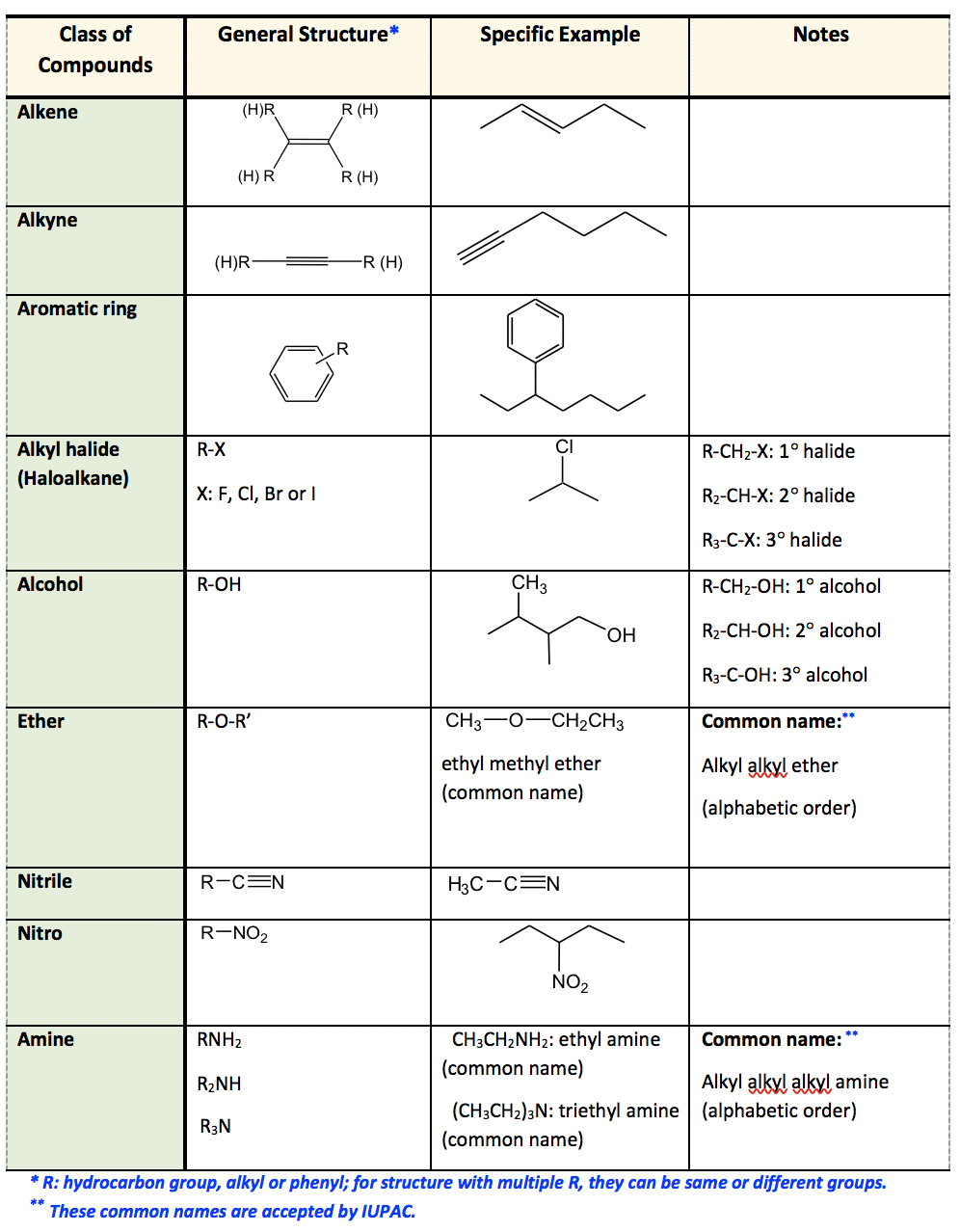 kpu.pressbooks.pubOrganic Functional Groups Chart – Expanded Edition | M A N O X B L O G
kpu.pressbooks.pubOrganic Functional Groups Chart – Expanded Edition | M A N O X B L O G
 manoxblog.comchemistry compounds compoundchem molecules forensic laboratory iaq chimie organique requests explorations
manoxblog.comchemistry compounds compoundchem molecules forensic laboratory iaq chimie organique requests explorations
4.2: The Functional Group - Chemistry LibreTexts
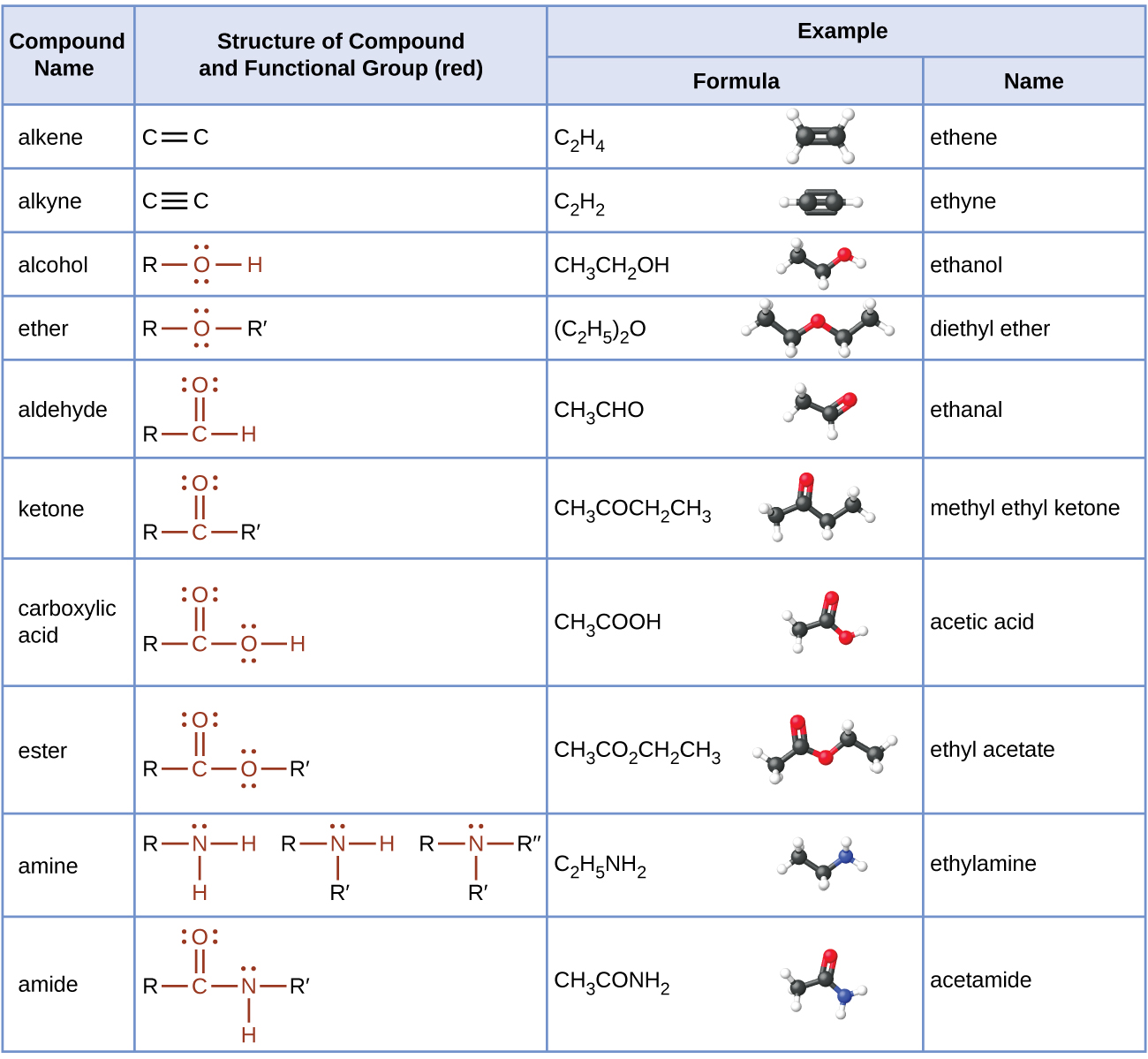 chem.libretexts.orgchemistry chem amines amides amine amide cnx compounds formulas structural libretexts identifying carboxylic pageindex aldehyde ketone ether atom include alkene
chem.libretexts.orgchemistry chem amines amides amine amide cnx compounds formulas structural libretexts identifying carboxylic pageindex aldehyde ketone ether atom include alkene
Organic chemistry classes with structure. Organic functional groups chart – expanded edition. Chemistry compounds compoundchem molecules forensic laboratory iaq chimie organique requests explorations